Sort by
Customise ColumnsFeature View
Show
| Part Number | Manu. | Model | Offer Price | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Grant special offer - Bioreactor Grant RTS-1 UK, real-time bacterial/yeast cultivation, strain screening, inhibition/toxicity, media optimization, synthetic biology, single-use vessel configuration, batch, system capacity 5mL to 30mL, reverse-spin, chain up to 12 units via USB, with parameter control in Temperature, Agitation Speed and Viable Cell Density OFFER ENDS 24-12-2025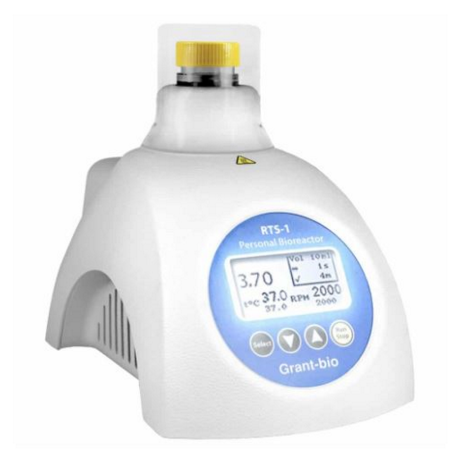  |
*Popular*RTS-1UK
Grant special offer - Bioreactor Grant RTS-1 UK, real-time bacterial/yeast cultivation, strain screening, inhibition/toxicity, media optimization, synthetic biology, single-use vessel configuration, batch, system capacity 5mL to 30mL, reverse-spin, chain up to 12 units via USB, with parameter control in Temperature, Agitation Speed and Viable Cell Density OFFER ENDS 24-12-2025 |
Grant | RTS-1 UK | Bacterial/yeast cultivation | Single-use | Batch | 5 | 0.03 | £2278.00 |
Grant special offer - Bioreactor Grant RTS-1C UK, temperature profiling & stress experiments with real-time bacterial/yeast cultivation, strain screening, inhibition/toxicity, media optimization, synthetic biology, single-use vessel configuration, batch, system capacity 5mL to 30mL, reverse-spin, chain up to 12 units via USB, with parameter control in Temperature, Agitation Speed and Viable Cell Density OFFER ENDS 24-12-2025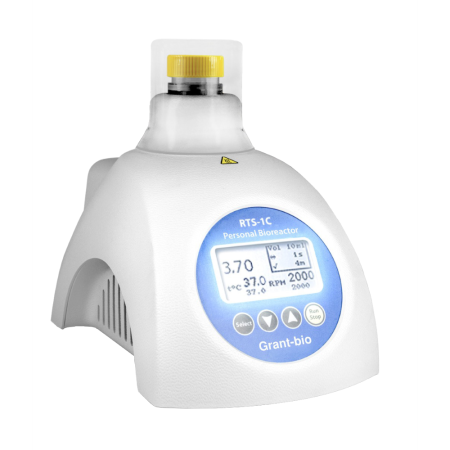  |
*Offer*RTS-1CUK
Grant special offer - Bioreactor Grant RTS-1C UK, temperature profiling & stress experiments with real-time bacterial/yeast cultivation, strain screening, inhibition/toxicity, media optimization, synthetic biology, single-use vessel configuration, batch, system capacity 5mL to 30mL, reverse-spin, chain up to 12 units via USB, with parameter control in Temperature, Agitation Speed and Viable Cell Density OFFER ENDS 24-12-2025 |
Grant | RTS-1C UK | Temperature profiling/stress experiments | Single-use | Batch | 5 | 0.03 | £2530.00 |
Wolf special offer - Bioreactor Grant RTS-8, fermentation kinetics, clone/protein expression screening, media optimization, temperature stress profiling, inhibition/toxicity tests, strain QC, systems biology, process optimization, single-use vessel configuration, batch, system capacity 3mL to 50mL, reverse-spin, 8 tubes per unit, with parameter control in temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen control, agitation speed and viable cell density OFFER ENDS 30-09-2025 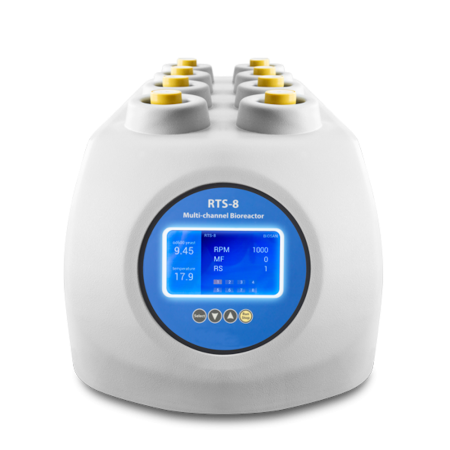 |
*Offer*RTS8
Wolf special offer - Bioreactor Grant RTS-8, fermentation kinetics, clone/protein expression screening, media optimization, temperature stress profiling, inhibition/toxicity tests, strain QC, systems biology, process optimization, single-use vessel configuration, batch, system capacity 3mL to 50mL, reverse-spin, 8 tubes per unit, with parameter control in temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen control, agitation speed and viable cell density OFFER ENDS 30-09-2025 |
Grant | RTS-8 | Fermentation | Single-use | Batch | 3 | 0.05 | £15097.00 |
Wolf special offer - Bioreactor TECNIC eLAB Advanced, upstream bioprocessing, multi-use/single-use vessel configuration, batch/perfusion, system capacity 250mL to 10L, with parameter control in Temperature, pH, Dissolved Oxygen, Level / Foam, Agitation Speed, Redox, TOC, Viable Cell Density, pCO, External Balance, Off-Gas Analyzer, impeller agitation system, cassette, hollow fibre and ceramic filtration capabilities, high modularity & scalability, includes machine commissioning and DDP delivery (Please contact us about sensors because some can be added at additional cost) OFFER ENDS 30-09-2025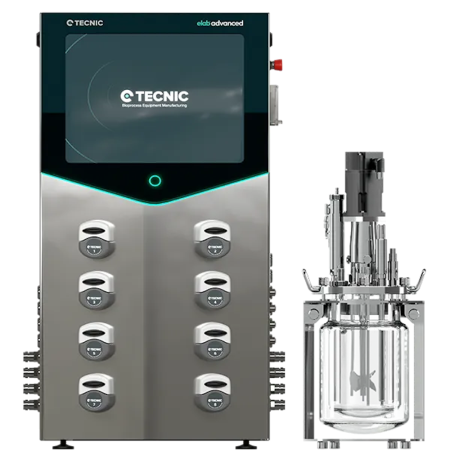  |
*Offer*ELABADV-BIO010
Wolf special offer - Bioreactor TECNIC eLAB Advanced, upstream bioprocessing, multi-use/single-use vessel configuration, batch/perfusion, system capacity 250mL to 10L, with parameter control in Temperature, pH, Dissolved Oxygen, Level / Foam, Agitation Speed, Redox, TOC, Viable Cell Density, pCO, External Balance, Off-Gas Analyzer, impeller agitation system, cassette, hollow fibre and ceramic filtration capabilities, high modularity & scalability, includes machine commissioning and DDP delivery (Please contact us about sensors because some can be added at additional cost) OFFER ENDS 30-09-2025 |
Tecnic | eLAB Advanced | Upstream bioprocessing | Multi-use/Single-use | Batch/Perfusion | 250 | 10 | £70888.00 |













